Linked List
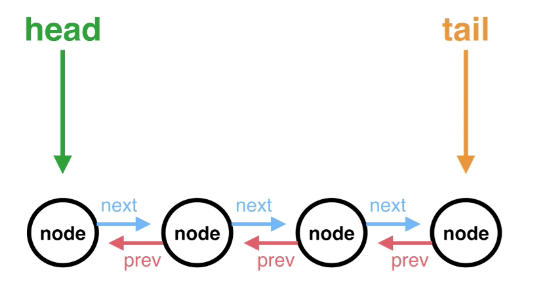
What is a Linked List?
List of elements called nodes connected (linked) together in a single file line.
Linked list only needs to know about the head and tail nodes for it to function correctly.
- Also see: https://visualgo.net/en/list?slide=1
Types of Linked Lists?
Singly linked list
- each node only has reference to the node after it (next node)
Doubly linked list
- each node has a reference to the next node AND to the previous node
Circular linked list
- head and tail of linked list are connected
Performance of Linked Lists
- adding/removing from head: O(1) | Constant Time | O of 1
- adding/removing from tail: O(1) | Constant Time | O of 1
- searching linked list: O(n) | Linear Time | O of n
Memory Management and Linked Lists
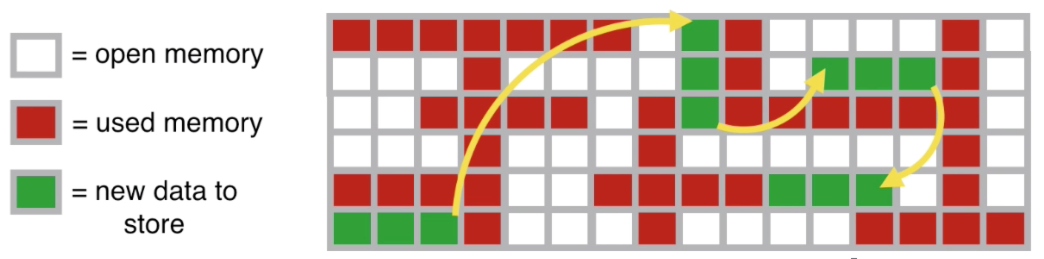
Linked list are a good data structure to use in languages that deal with physical memory space (javascript)
- they allow you to break data into little pieces
- pieces can be spread across different areas
- don't necessarily have to be stored together
Use Cases of Linked Lists
- online gaming
- poker
- circular list of players
- additional pointers for
- active player
- dealer
- big blind
- small blind
- board games, dominoes
Javascript Linked List
// Linked List Constructor Function
function LinkedList() {
this.head = null; // will be of type Node
this.tail = null; // will be of type Node
}
// Node Constructor Function
function Node(value, next, prev) {
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
this.prev = prev;
}
LinkedList.prototype.addToHead = function (value) {
// create new node, since we are adding to head prev is null
var newNode = new Node(value, this.head, null);
if (this.head) {
// if item exists in head
this.head.prev = newNode; // add new node to it's 'prev' property
} else {
// else nothing currently exists
this.tail = newNode; // and the new item will also be the tail
}
this.head = newNode; // set new node to head of list
};
LinkedList.prototype.addToTail = function (value) {
// create new node, since we are adding to tail next is null
var newNode = new Node(value, null, this.tail);
if (this.tail) {
// if item exists in tail
this.tail.next = newNode; // add new node to it's 'next' property
} else {
// else nothing currently exists
this.head = newNode; // and the new item will also be the head
}
this.tail = newNode; // set new node to tail of list
};
LinkedList.prototype.removeHead = function () {
// if list is empty return null
if (!this.head) {
return null;
}
var val = this.head.value; // save current head value
this.head = this.head.next; // set head pointer to be the next node
// check head exists, we could have removed the only node
if (this.head) {
this.head.prev = null; // remove prev pointer on new head node
} else {
// else we removed the only node
this.tail = null; // so we set tail to null
}
// return removed node value
return val;
};
LinkedList.prototype.removeTail = function () {
// if list is empty return null
if (!this.tail) {
return null;
}
// save current tail value
var val = this.tail.value;
// set tail pointer to be the node prev to current tail node
this.tail = this.tail.prev;
// if list isn't empty, we could have removed only node
if (this.tail) {
// new tail is last item in list, remove next pointer on new tail node
this.tail.next = null;
} else {
// we removed the only node
this.head = null; // so we set head to null
}
// return removed node value
return val;
};
LinkedList.prototype.search = function (searchValue) {
var currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode) {
if (currentNode.value === searchValue) {
return currentNode.value;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next; // if null it won't continue while loop
}
return null;
};
LinkedList.prototype.indexOf = function (value) {
var indexes = [];
var currentIndex = 0;
var currentNode = this.head;
while (currentNode) {
if (currentNode.value === value) {
indexes.push(currentIndex);
}
currentIndex++;
currentNode = currentNode.next; // if null it won't continue while loop
}
return indexes;
};
var ll = new LinkedList();